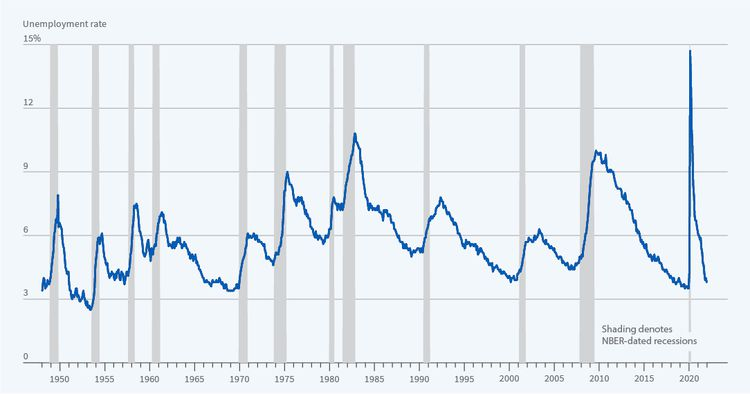
As concerns about a U.S. economy recession loom, the specter of declining consumer confidence and erratic trade policies raises alarm bells among economists. The recent turmoil in the stock market, exacerbated by escalating trade war tensions with key partners like China, has led many to question the stability of the American financial landscape. Coupled with low readings on the consumer sentiment index, these factors indicate potential vulnerabilities that could deepen this economic downturn. Furthermore, as the Federal Reserve deliberates on interest rate adjustments, the outcomes of these decisions will have significant ramifications for economic recovery predictions. With uncertainty dominating market narratives, understanding the interplay between these elements is crucial for investors and policymakers alike.
As we assess the current landscape of the American financial environment, it becomes increasingly important to address the signals of a potential economic downturn in the United States. The intersection of declining consumer confidence and heightened market volatility raises important questions about the sustainability of growth. Analysts are observing critical indicators, such as changes in federal monetary policy and external economic pressures, which could significantly influence recovery trajectories. Amidst market instability, alternative perspectives shed light on how global interactions, such as trade disputes, may further complicate the nation’s economic resilience. Understanding these dynamics is essential for navigating uncertainties and developing effective strategies for future prosperity.
Understanding the U.S. Economy Recession Risks
The current state of the U.S. economy indicates a heightened risk of recession, as warned by leading economists. Factors such as an ongoing trade war and unpredictability surrounding the Federal Reserve’s interest rates contribute significantly to this outlook. The recent downturn in the University of Michigan’s consumer sentiment index reflects a growing concern among consumers, hinting at potential cutbacks in spending that could exacerbate economic conditions. With the looming threat of tariffs impacting various sectors, businesses and consumers alike are stepping back, leading to an environment fraught with uncertainty.
Analysts predict that if the recession materializes, it could be detrimental not only to consumer confidence but also to overall economic growth. Each day, uncertainty around government policy and tariff implementations place an additional strain on market stability. The potential for a prolonged economic slowdown is exacerbated by anxiety surrounding stock market fluctuations and the possibility of further interest rate changes by the Federal Reserve, tightening financial conditions just as faith in economic recovery begins to wane.
The Impact of Trade Wars on the U.S. Economy
Trade wars have historically been a source of economic tension that can lead to significant downturns. The recent tariffs imposed by countries like China, Canada, and Mexico in retaliation to U.S. policies are causing ripples across various industries—a stark reminder of how interconnected global markets are. Economists argue that while tariffs may be introduced as protective measures for domestic industries, they ultimately lead to increased prices for consumers and diminished trade relationships. These trade tensions not only impact the flows of goods but can also create long-lasting reservations among foreign investors regarding the U.S. market.
Moreover, the implications of these trade wars extend beyond immediate financial metrics. The economic uncertainty they create can stymie investment and hiring, leading corporate leaders to adopt a ‘wait and see’ approach. Companies are less likely to make significant financial commitments amidst fears that the trade climate could worsen, subsequently stalling economic growth and delaying any potential for recovery influenced by strong consumer sentiment.
Stock Market Conundrums Amid Economic Uncertainty
The stock market, often seen as a bellwether for economic health, has recently faced severe fluctuations reflecting deep-rooted concerns regarding the state of the U.S. economy. Market analysts point to a combination of factors, including escalating trade tensions and inconsistent fiscal policies, as primary contributors to recent selloffs. As investors grapple with volatility, many are reevaluating their positions in the marketplace, leading to sustained uncertainty and risk aversion. Stock market concerns highlight underlying fears of recession, where unexpected drops can have a cascading effect on consumer confidence and spending.
The Federal Reserve’s monetary policy decisions play a crucial role in this delicate balance. As they deliberate on interest rate adjustments, the ramifications they hold for both stock valuations and overall economic sentiment are substantial. A cautious approach to interest rates could ease some market fears, but the potential for inflation remains a pressing issue that may restrain aggressive rate cuts. Thus, the stock market remains in a precarious position, influenced heavily by both domestic policy measures and external economic forces.
Federal Reserve Interest Rates: A Double-Edged Sword
The Federal Reserve’s interest rate policy has a profound effect on the broader economy. Current debates reflect the tension between supporting economic growth by lowering rates and controlling inflation by keeping them elevated. In response to ongoing market turbulence, the Fed faces the critical decision of whether to reduce rates to stimulate investment and consumer spending or maintain higher rates to curb rising inflation expectations. This dilemma underscores a unique economic environment characterized by both stimulus and restraint.
Adjusting interest rates is not without its complexities, especially in the current economic climate, where uncertainties reign from trade wars and shifting consumer sentiments. Rate cuts could indeed invigorate segments of the economy, but they also pose risks related to inflation, creating a challenging balancing act for policymakers. The decisions made by the Federal Reserve in the coming months will be vital as they can either pave the way for recovery or exacerbate recessionary tendencies, making their role paramount in shaping the U.S. economic landscape.
Consumer Sentiment Index: Indicator of Economic Health
The University of Michigan’s consumer sentiment index serves as a key indicator of economic health and consumer confidence. Recently, this index has reported its lowest levels since late 2022, suggesting that American consumers are feeling increasingly uneasy about the financial future. As consumers begin to pull back on spending—often a leading driver of economic growth—the implications for both businesses and the overall economy can be profound. A decline in this index signals a hesitance among individuals to invest in larger purchases or even engage in day-to-day spending.
Understanding fluctuations in the consumer sentiment index is crucial for predicting economic trends. When consumers exhibit heightened levels of fear or uncertainty due to factors such as job loss or instability in stock markets, their spending habits invariably change. This shift results in lower demand for goods and services, potentially inviting further economic contractions. Hence, business leaders and policymakers must closely monitor consumer sentiment as it directly aligns with the trajectory of both the economy and future recovery efforts.
Economic Recovery Predictions: Navigating Uncertain Waters
As analysts forecast the potential paths toward economic recovery, the prevailing sentiment is one of caution. Predictions surrounding the U.S. economy’s resilience are often tempered by underlying factors such as trade tensions and consumer sentiment. Many experts suggest that without swift resolution to ongoing trade disputes and a clear fiscal policy, recovery may lag behind expectations. The interconnectedness of the global economy means that international events can swiftly turn optimistic forecasts into pessimistic realities, complicating recovery efforts.
Additionally, the outlook is often shaped by how effectively government policies address burgeoning issues like inflation and employment stability. Uncertainty can linger if the Federal Reserve is indecisive with interest rate policies, leading to a potential stagnation in growth during crucial periods. As forecasts shift in response to market conditions and external pressures, stakeholders must remain adaptable to navigate this landscape and contribute to fostering a more robust economic recovery.
The Role of Government Spending in Economic Stability
Government spending plays a pivotal role in bolstering economic stability during uncertain times. Recent cuts proposed by politicians raise alarms about potential negative repercussions for the economy, particularly amidst heightened anxiety about the recession. A reduction in government outlays can directly lead to decreased aggregate demand, stifling growth and potentially leading to higher unemployment rates. This dynamic underscores the importance of maintaining balanced fiscal policies that enable investments in infrastructure and social programs essential for long-term growth.
Moreover, as financial pressures mount, effective government spending can stimulate the economy by providing crucial support to various sectors. Targeted investments in technology and education can create jobs and enhance productivity, yielding positive economic outcomes. However, if spending approaches are overly restrictive, they may hinder recovery efforts and contribute to the cyclicality of economic downturns. Thus, finding a suitable equilibrium in government spending is essential for maintaining both economic growth and societal welfare.
Investor Behavior in Times of Economic Strain
Investor behavior during periods of economic instability tends to gravitate toward caution and risk aversion. With a volatile stock market and concerns about the looming recession, many investors are likely reassessing their asset allocations and strategies, often leading to increased safety measures such as moving investments toward bonds or more stable sectors. Such behavior reflects a natural response to uncertainty, where anticipated risks discourage investments in equities that may experience heightened volatility.
Furthermore, sentiment can shift dramatically based on news regarding tariffs, fiscal policies, or actions taken by the Federal Reserve. Market investors grow sensitive to these changes and react swiftly, often driving prices down during periods of uncertainty. This creates a feedback loop where increased volatility leads to more cautious investor behavior, thereby exacerbating the situation. A thorough understanding of market psychology is vital for investors during these uncertain times, highlighting the need for responsive and informed investment strategies.
Long-term Effects of Economic Policies
The long-term effects of current economic policies cannot be overstated, as they shape the future landscape of the U.S. economy. Tariff implementations, trade policies, and fiscal decisions made today can ripple through various sectors, influencing everything from consumer behavior to international competitiveness. The impact of these policies may not be immediate, but their consequences will undoubtedly be felt in years to come, determining the rate of recovery or progression into a potential recession.
Evaluating the outcomes of economic decisions made during tumultuous periods could offer lessons for future policymakers. Understanding how current tariffs are affecting job markets, investment patterns, and overall economic growth will provide valuable insights into how governance can effectively stabilize economies in distress. Therefore, ongoing analysis of these policies will enable leaders to adapt and innovate towards sustainable economic growth in the years ahead.
Frequently Asked Questions
What impact does the trade war have on the U.S. economy recession risk?
The ongoing trade war significantly increases the risk of a U.S. economy recession. Tariffs imposed by trade partners like China and Canada lead to higher consumer prices and decreased demand for American goods, which in turn can slow economic growth and consumer spending. This environment fosters uncertainty among investors and affects market confidence, heightening recession fears.
How do stock market concerns relate to the U.S. economy recession?
Stock market concerns play a critical role in forecasting a U.S. economy recession. A declining stock market can signal reduced investor confidence and lead to lower levels of investment, which may contribute to economic slowdown. If market losses persist, it can trigger a negative feedback loop, impacting consumer spending and potentially leading to a recession.
What is the Federal Reserve’s role in addressing U.S. economy recession fears related to interest rates?
The Federal Reserve has a pivotal role in managing U.S. economy recession fears by adjusting interest rates. During economic slowdowns, the Fed typically lowers interest rates to encourage borrowing and spending. However, amidst rising inflation concerns, they face a challenging decision on whether to cut rates or keep them stable to avoid exacerbating inflation, which is critical during recessionary periods.
How does the consumer sentiment index reflect the chances of a U.S. economy recession?
The consumer sentiment index is a crucial indicator for predicting a U.S. economy recession. A declining consumer sentiment signals waning consumer confidence, potentially leading to reduced spending and investment. As consumers become more cautious during uncertain economic conditions, it can catalyze a downturn, making the prospect of a recession more likely.
What are the predictions for economic recovery amidst recession fears in the U.S.?
Economic recovery predictions amidst U.S. economy recession fears are mixed. Factors like ongoing tariffs, stock market volatility, and Federal Reserve interest rate policies all influence potential recovery timelines. While some economists remain hopeful about a rebound due to past recovery patterns, current uncertainties suggest that recovery may take longer and could require significant policy intervention.
| Key Points |
|---|
| U.S. economy faces potential recession warnings driven by trade war tensions, stock market declines, and low consumer confidence. |
| Actions by China, Mexico, and Canada in response to U.S. tariffs could escalate market uncertainties and downturns. |
| Economists largely oppose tariffs; however, they may have some limited justifications in specific contexts like protecting infant industries. |
| The Federal Reserve’s dilemma: maintaining interest rates to control inflation while supporting economic growth. |
| Indicators such as the University of Michigan consumer sentiment index suggest declining economic confidence, potentially leading to a recession. |
| Current government policies may be contributing to uncertainty, advising a need to monitor developments closely. |
Summary
The U.S. economy recession is a pressing concern as various indicators signal a potential downturn. Factors such as escalating trade wars, and declining consumer sentiment point towards a negative economic trajectory. With the Federal Reserve facing tough choices on interest rates amidst market volatility, the path forward remains uncertain. Continuous monitoring of fiscal policies and global market reactions will be crucial in understanding the depth and length of any economic recession.