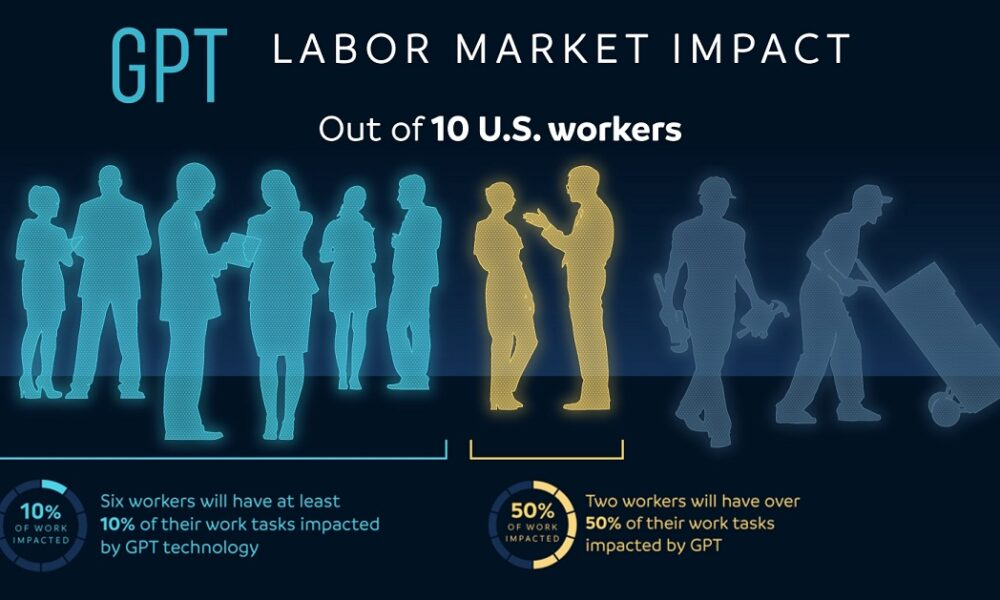
The impact of AI on the labor market is undeniable and increasingly complex, reflecting how technology in the workforce continues to evolve. Recent studies indicate that artificial intelligence isn’t just a temporary trend; it’s reshaping job structures and economic dynamics across various industries. Despite fears of job displacement and AI taking over, there’s a simultaneous rise in demand for skilled positions that suggest a dual pathway of occupational churn. The economic impacts of AI are multifaceted, influencing everything from compensation structures to the skill sets required in the workplace. As sectors adapt to these changes, understanding AI trends in jobs becomes crucial for both employers and employees navigating this shifting landscape.
Examining the influence of AI on employment reveals a transformative force in the professional environment. This phenomenon could be seen as a technological revolution similar to the advent of computers or the rise of industrial machinery, which fundamentally altered the dynamics of job availability and job roles. The conversation around occupational transitions highlights the need for workers to adapt to new economic paradigms shaped by automation and AI advancements. While concerns around job security remain, the rise of high-skilled STEM occupations indicates that innovation is also creating new opportunities. Ultimately, this evolution in the labor landscape emphasizes the importance of resilience and adaptation to ensure that individuals thrive amid ongoing changes.
Understanding AI’s Impact on the Labor Market
The impact of artificial intelligence (AI) on the labor market is gradually unfolding as researchers like David Deming and Lawrence H. Summers explore the historical context of technological disruption. Their study flags significant trends, noting a shift in job dynamics from stability to potential upheaval. Around the late 2010s, AI began to influence occupational structures, promoting high-skill jobs over low-paid roles. This transition underscores the importance of upskilling the workforce to adapt to new demands as automation technologies reshape job capabilities.
As AI technology continues to penetrate various sectors, it is crucial to recognize the economic impacts of AI. Many roles once considered secure are now subject to the threat of job displacement as firms increasingly invest in AI-driven technologies. This creates a dual reality where workers with advanced skills, especially in STEM fields, are thriving, while those in low-skill service jobs face potential unemployment. The challenge lies in balancing the workforce through education and training initiatives to navigate this economic transition.
The Role of Technology in Workforce Transformation
Technology has played a crucial role in transforming the workforce, particularly seen in the way automation and AI have redefined various job functions. From the introduction of computers to the latest advancements in robotic process automation, each technological wave has altered the job landscape. The study highlights how the adoption of keyboards, for example, transitioned many jobs into roles requiring less manual entry and more cognitive skills, leading to greater efficiency in the labor market.
However, this transformation has led to occupational churn, where specific jobs fade away while new ones emerge. As industries evolve under the influence of frontier technologies, the demand for tech-savvy employees is surging. The rising comparison of low-skill roles with highly trained positions indicates a growing divide in the workforce, reflecting wages and job security that favor individuals with robust technical training.
The Eight Trends of Job Polarization and Recovery
Job polarization has emerged as a significant trend in the current labor market, highlighting a divergence of employment opportunities based on skill levels. With AI and automation automating low-skilled functions, a notable increase in high-skilled jobs has been observed. The Harvard study points out that while the labor market once saw growth in both low and high-paying jobs, recent trends indicate a resurgence of well-compensated roles that require advanced training, opening new avenues for economic advancement.
As a result, industries are seeing a revived interest in hiring skilled labor, particularly within the technology and engineering sectors. This dynamic may suggest that while certain occupations face decline due to automation, others are evolving. Workers willing to adapt and gain new skills can harness economic growth, demonstrating that AI’s role is not merely one of displacement, but also of opportunity for an empowered, future-ready workforce.
Analyzing Economic Impacts of AI Development
The economic impacts of AI development have sparked widespread discussions among economists and job market analysts. The shift from manual labor to machine-driven processes raises critical questions about the future of job security. While some fear mass displacement due to rapidly advancing technology, the stability observed in certain sectors between 1990 and 2017 contradicts this narrative. The introduction of AI may foster productivity and innovations that can bolster the economy, despite job losses in specific fields.
Furthermore, as firms channel investments towards AI, the implications for the broader economy become more pronounced. The increase in skilled positions, particularly in STEM, highlights a necessary pivot toward advanced education. With better training in technology, workers not only protect their positions but also contribute to driving economic growth, illuminating the dual role of AI as both a challenge and an economic catalyst.
Automation Anxiety and Its Challenges
Automation anxiety refers to the widespread concern that advancements in technology, especially AI, will render many jobs obsolete. Studies predicting potential job losses have instilled a sense of urgency among workers to adapt to the changing landscape. As highlighted in the research findings, although the pace of automation slowed from 1990 onward, the potential for increased job displacement has returned, necessitating a proactive approach towards reskilling and retooling the workforce.
Moreover, understanding that disruption is one part of the broader economic picture is vital. While some jobs will inevitably vanish, this does not preclude the emergence of new employment avenues. Facilitating transitions for the workforce, such as investing in retraining programs, can mitigate the anxiety surrounding automation and empower workers to explore new opportunities created by technological advancements.
Navigating the Shift Toward STEM Jobs
The shift toward science, technology, engineering, and math (STEM) jobs is becoming increasingly pronounced as companies seek expertise in AI and related technologies. The research demonstrates a remarkable increase in the STEM job share within the labor market, indicating strong market demand for technically proficient workers. This trend presents a positive outlook for the economy, as innovation-driven positions become pivotal in driving competitive advantage.
Consequently, the rise of STEM careers reinforces the necessity for educational institutions and training programs to recalibrate their curriculums. By focusing on skills pertinent to emerging technologies, the workforce can better position itself to meet the demands of an evolving job market. As demand for STEM professionals soars, strategies to attract and train talent in these fields will enhance economic resilience and workforce adaptability.
The Future of Low-Paid Service Jobs
Low-paid service employment is undergoing significant scrutiny in the context of technological advancement. The decline in these roles since 2019 coincides with the rise of AI, which appears to be automating functions previously held by humans. This reduction raises pressing questions about the sustainability of low-wage jobs as firms lean heavily into technologies that replace human labor.
In response to these changes, businesses must consider how best to support their workforce through transitions. While some service positions may never return in their former capacity, evolving customer expectations and technological capabilities could lead to a redefined service industry that combines human interaction with automated efficiency. Fostering an environment that values retraining and support can help navigate these shifts, benefiting both employees and employers.
Adapting to Job Displacement Trends
Adapting to the trends of job displacement due to AI is critical for various stakeholders within the labor market. Organizations need to recognize that while automation can improve efficiency, it also poses risks for employees in roles prone to becoming obsolete. The recent findings suggest that businesses become more selective and expect higher productivity from workers as they integrate AI solutions, underscoring the need for a workforce proficient in navigating technology-driven environments.
For individual employees, this necessitates a mindset of continuous learning and adaptation. Upskilling initiatives that focus on critical thinking and technological proficiency will become essential in maintaining job relevance. Workers must embrace lifelong learning to thrive amidst these transitions, enabling them to compete in a landscape that values innovation and specialist knowledge.
Preparing for the Next Economic Disruption
As we look toward the future, preparing for the next economic disruption influenced by AI and automation becomes essential for both individuals and companies. The historical perspective reveals that while technology has traditionally prompted job shifts, the current scale and pace of change herald unique challenges. Economic volatility, often spurred by technological advancements, necessitates proactive workforce strategies to ensure sustainability and adaptability.
Preparing for such disruptions involves not only reskilling and upskilling but fostering a culture that promotes agile thinking and innovation within organizations. By anticipating shifts and equipping employees with relevant skills, companies can navigate potential upheavals more effectively. Thus, engaging in foresight and strategic planning today can bolster resilience against future labor market fluctuations influenced by AI.
Frequently Asked Questions
How is AI impacting the labor market in the U.S. today?
AI is significantly affecting the labor market by driving changes in occupational churn and job distribution. Recent studies indicate an increasing demand for skilled positions, particularly in STEM fields, as businesses invest heavily in AI technologies, leading to structural changes in job availability.
What are the economic impacts of AI on job displacement?
The economic impacts of AI on job displacement include a decline in low-paid service and retail jobs, while growth is observed in high-paid, technical roles. As AI technologies advance, many lower-skill positions may face significant reductions, prompting a shift in the workforce towards higher-skilled jobs.
What trends are emerging regarding technology in the workforce due to AI?
Emerging trends related to technology in the workforce include an upward shift toward high-compensation jobs requiring advanced skills and a notable increase in STEM opportunities. Additionally, there is a decline in low-wage roles, impacted heavily by AI and e-commerce advancements.
Are we witnessing occupational churn influenced by AI trends in jobs?
Yes, recent findings suggest that occupational churn is being influenced by AI trends. Increased investments in AI have correlated with significant changes in job structures, particularly favoring skilled labor while diminishing roles traditionally filled by lower-skilled workers.
What role does AI play in job polarization within the labor market?
AI is contributing to the end of job polarization by facilitating the growth of high-paying, skilled jobs, contrasting with the decline of middle-income positions. This shift indicates a transformation in the labor market landscape influenced by technological advancements and AI integration.
How has the pandemic accelerated the impact of AI on the labor market?
The pandemic acted as an accelerant for AI’s impact on the labor market by increasing the reliance on e-commerce and AI-driven technologies. This shift has changed consumer behavior, leading to a quicker adoption of online shopping and diminishing demand for brick-and-mortar retail roles.
What future should workers anticipate concerning AI and labor market changes?
Workers should anticipate a dynamic labor market increasingly influenced by AI, which could result in higher productivity expectations and potential job displacement, especially for roles susceptible to automation. Upskilling and adaptability will be crucial for long-term career viability.
How can knowledge workers prepare for changes driven by AI in their sectors?
Knowledge workers can prepare for AI-driven changes in their sectors by enhancing their technical skills, embracing AI tools in their workflows, and developing a mindset of continuous learning to remain competitive and relevant in an evolving job landscape.
| Key Trend | Description |
|---|---|
| Automation Anxiety | Many believed that AI would replace jobs rapidly, with studies claiming that 47% of U.S. occupations were at risk of being displaced by computers. |
| Reduction of Low-Paid Jobs | AI has contributed to the decline of low-paid service jobs, particularly after 2019. |
| Growth of STEM Jobs | A significant increase in STEM jobs, which rose from 6.5% in 2010 to nearly 10% in 2024. |
| Decline in Retail Sales Jobs | The share of retail sales jobs fell from 7.5% to 5.7% between 2013 and 2023, attributed to the rise of e-commerce and AI. |
| End of Job Polarization | A shift from a barbell-shaped job market pattern to increased growth in high-paid jobs requiring skills. |
Summary
The AI impact on the labor market has begun to reveal complex dynamics that could transform various professions. While earlier narratives suggested a future dominated by automation, recent studies indicate that there is a nuanced shift occurring. Economists have highlighted several key trends such as the decline of low-paid jobs, a notable increase in STEM roles, and the gradual disappearance of retail positions due to technology. As AI continues to advance, it becomes increasingly clear that while it can enhance productivity, it also poses risks of job displacement for certain sectors, urging a reevaluation of workforce strategies across industries.